What is KASAN?
KASAN is a combination of kernel and compile time modifications that result in an instrumented system that allows for simpler bug discovery and root cause analysis.
KASAN can detect many types of memory violations in the kernel. It can also detect out-of-bound reads and writes on stack, heap and global variables, and can detect use-after-free and double frees.
Similar to ASAN, KASAN uses a combination of memory-function instrumentation at compile time and shadow memory to track memory accesses at runtime. In KASAN, an eighth of the kernel memory space is dedicated to shadow memory, which determines if a memory access is valid or not.
KASAN in Android Kernel
- Build a kernel with KASAN+KCOV
- create standalone toolchain
- build kernel
- KASAN in Android
- overview
- insight
Build a kernel with KASAN+KCOV
The following experiments are done in ubuntu 18.04.
- create standalone toolchain
Standalone Toolchains introduced how to setup a standalone toolchain. You can setup the toolchain as you want, e.g. ARM64 toolchain, x86_64 toolchain. For example, I created a toolchain of type x86_64 like:$NDK/build/tools/make_standalone_toolchain.py \ --arch x86_64 --api 28 --install-dir /tmp/my-android-toolchain -
build kernel Building Kernels introduced how to build a standalone kernel. I build a x86_64 kernel with the previous created toolchain.
- download goldfish source code
mkdir kernel cd kernel git clone https://android.googlesource.com/kernel/goldfish.git cd goldfish git branch -a git checkout remotes/origin/android-goldfish-4.9-devNotice: you can find all the kernel source code here
- enable kasan and kcov
- copy x86_64_defconfig(goldfish/arch/x86/configs/) to x86_64_kasan_kcov_defconfig.
- add the following flags into x86_64_kasan_kcov_defconfig:
CONFIG_KASAN=y CONFIG_KASAN_INLINE=y CONFIG_KCOV=y CONFIG_SLUB=y CONFIG_SLUB_DEBUG=y
- build with standalone toolchain
PATH = $PATH:/tmp/my-android-toolchain/bin/ export ARCH=x86_64 export CROSS_COMPILE=x86_64-linux-android- make x86_64_kasan_kcov_defconfig make
- download goldfish source code
KASAN in Android
- overview
- kasan files
- mm/kasan/kasan_init.c
- mm/kasan/kasan.c
- mm/kasan/kasan.h
- mm/kasan/quarantine.c
- mm/kasan/report.c
- include/linux/kasan.h
- include/linux/kernel.h
- arch/arm64/include/asm/kasan.h
- …
- how it works
kasan relies on
shadow memorywhich is eighth of the kernel memory space. Each shadow byte can represent 8 memory bytes. If the shadow byte is not 0 or pre-filled size related value, kasan reports catching a UAF, memory OOB read/write, double free or some other memory issue. kasan works for both heap and stack.
- kasan files
- kasan insight
-
for detecting OOB memory issue
kasan allocates additional redzone pages(left and right) for applied memory.
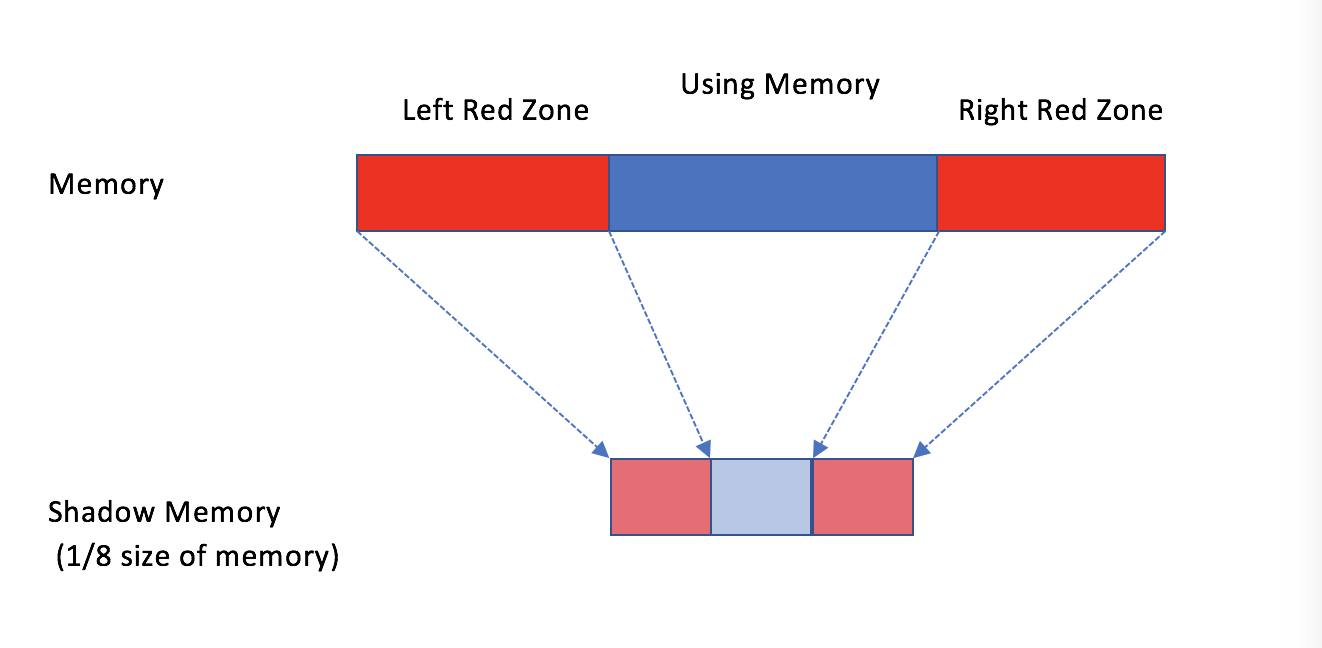 All virtual memory has its own mapped shadow memory, every 8 virtual memory bytes map to 1 shadow byte. When kasan is on, new allocated memory has left and right redzone. Redzone shadow memory is poisoned so that if you call memory operations such as memcpy or even simply bytes read/write, which access redzone, kasan can catch this illegal action.
All virtual memory has its own mapped shadow memory, every 8 virtual memory bytes map to 1 shadow byte. When kasan is on, new allocated memory has left and right redzone. Redzone shadow memory is poisoned so that if you call memory operations such as memcpy or even simply bytes read/write, which access redzone, kasan can catch this illegal action.For example,
memcpywith kasan on is :#undef memcpy void *memcpy(void *dest, const void *src, size_t len) { check_memory_region((unsigned long)src, len, false, _RET_IP_); check_memory_region((unsigned long)dest, len, true, _RET_IP_); return __memcpy(dest, src, len); }memcpy is just one trigger point that can trigger kasan check. check_memory_region checks whether the target memory scope is poisoned. Here, memcpy checks whether memory of [src, len] and [dst, len] is poisoned, if poisoned, kasan reports this illegal operation and panic the kernel.
As for memory poison check, it actually checks its shadow memory. All the shadow bytes of the memory is checked:- if it is 0, it is legal.
- if it is (memory size & 7), it is legal.
- all other values are illegal, e.g. 0xfe
There are many other trigger points, almost all the memory opertion can be a point. In Android kernel, there exists:
- memcpy
- memmove
- __asan_load1, __asan_load2, __asan_load4, __asan_load8, __asan_load16
- __asan_store1, __asan_store2, __asan_store4, __asan_store8, __asan_store16
- …
-
for detecting double free/UAF
when new memory is allocated, if the size is aligned with 8:
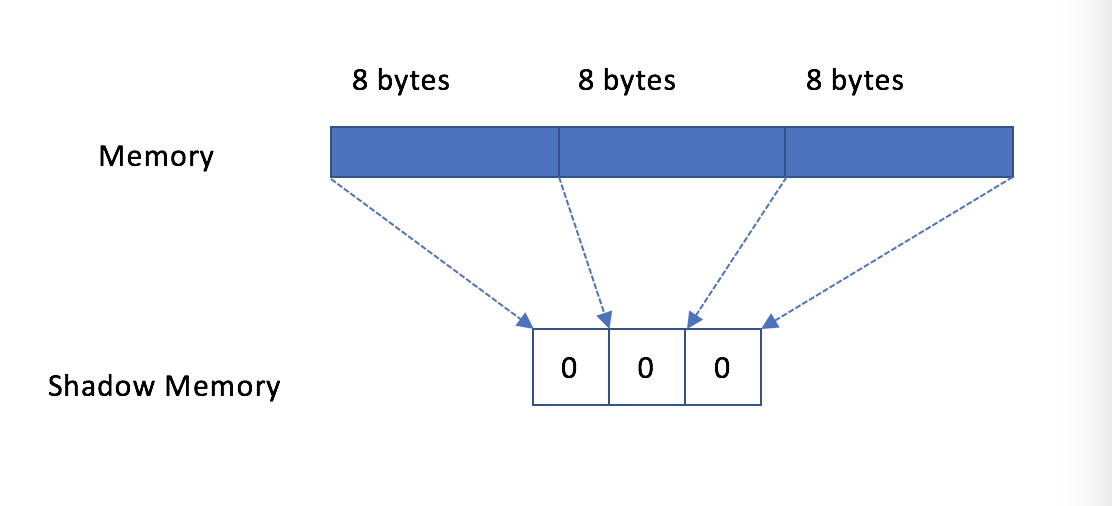
if the size is not aligned,
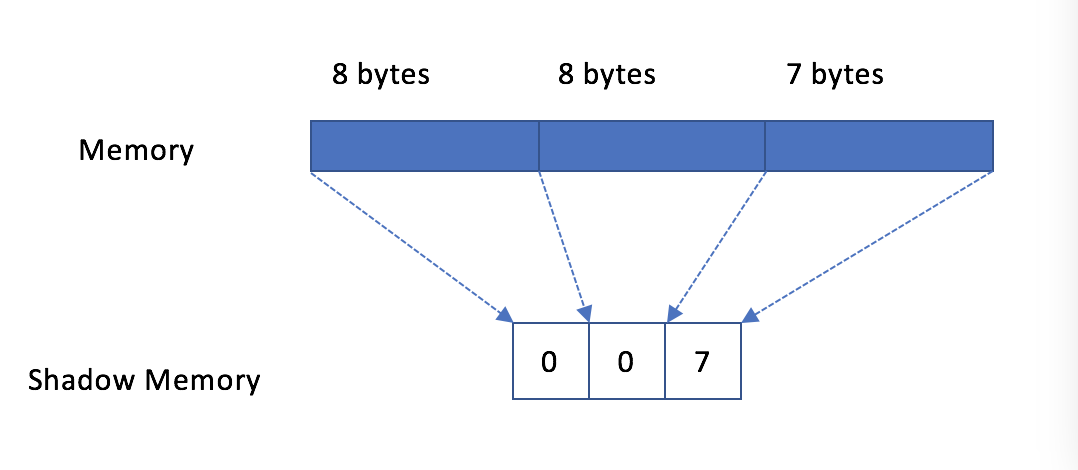
The last shadow byte is set to size&7.when the memory is freed, the shadow memory changes to:
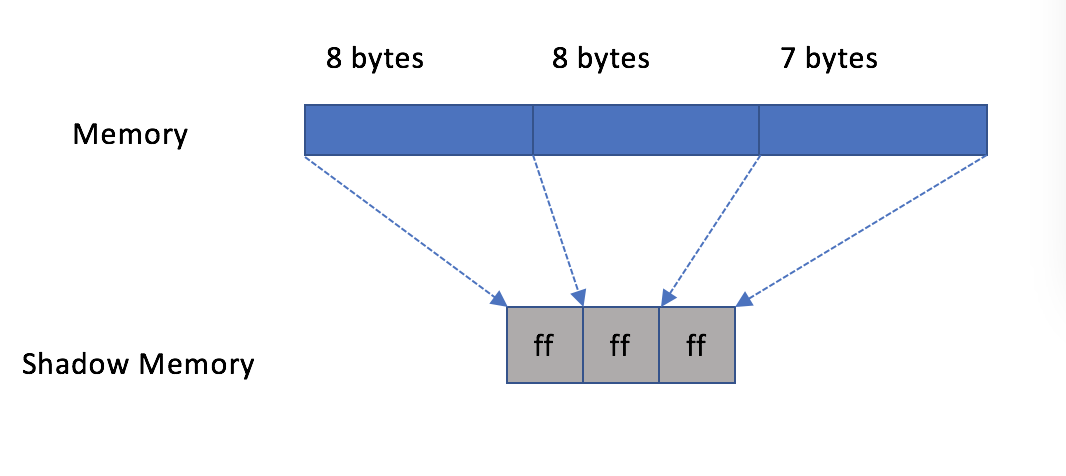
Now the shadow bytes all become 0xff(different status has different value), if UAF/double free occurs, memory opertion triggers kasan check, and the shadow bytes are illegal now, kasan gives report and panics the kernel.
In android kernel, the status can be:#define KASAN_FREE_PAGE 0xFF /* page was freed */ #define KASAN_PAGE_REDZONE 0xFE /* redzone for kmalloc_large allocations */ #define KASAN_KMALLOC_REDZONE 0xFC /* redzone inside slub object */ #define KASAN_KMALLOC_FREE 0xFB /* object was freed (kmem_cache_free/kfree) */ #define KASAN_GLOBAL_REDZONE 0xFA /* redzone for global variable */ /* * Stack redzone shadow values * (Those are compiler's ABI, don't change them) */ #define KASAN_STACK_LEFT 0xF1 #define KASAN_STACK_MID 0xF2 #define KASAN_STACK_RIGHT 0xF3 #define KASAN_STACK_PARTIAL 0xF4 #define KASAN_USE_AFTER_SCOPE 0xF8 -
- vmlinux with kasan/kcov ON
vmlinux can be found [here]